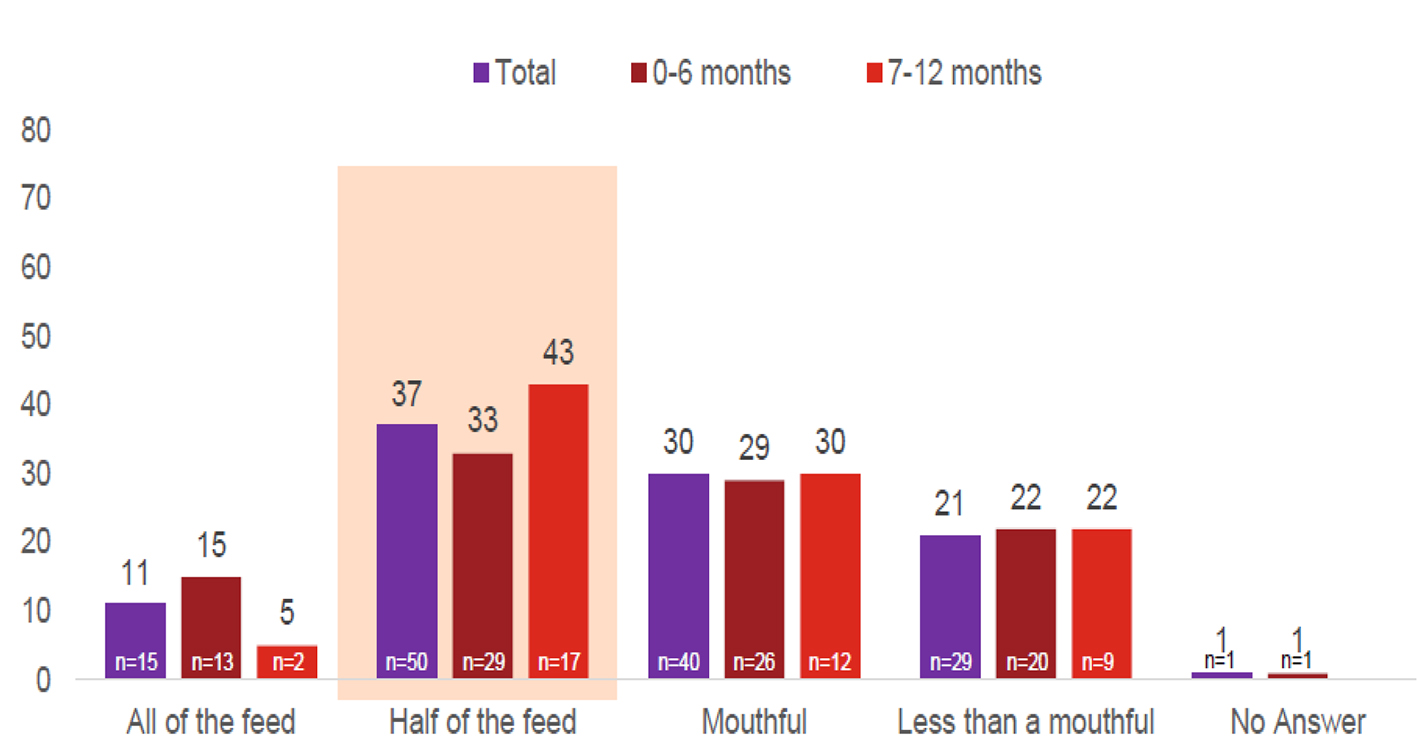
Figure 1. Reported average of regurgitation volume at baseline (%). Total interviews (n = 135); 0 - 6 months (n = 89); 7 - 12 months (n = 40).
| International Journal of Clinical Pediatrics, ISSN 1927-1255 print, 1927-1263 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Int J Clin Pediatr and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.theijcp.org |
Original Article
Volume 8, Number 1, August 2019, pages 1-7
Nutritional Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Among Infants in the Philippines: Insights From Real-World Evidence
Figures

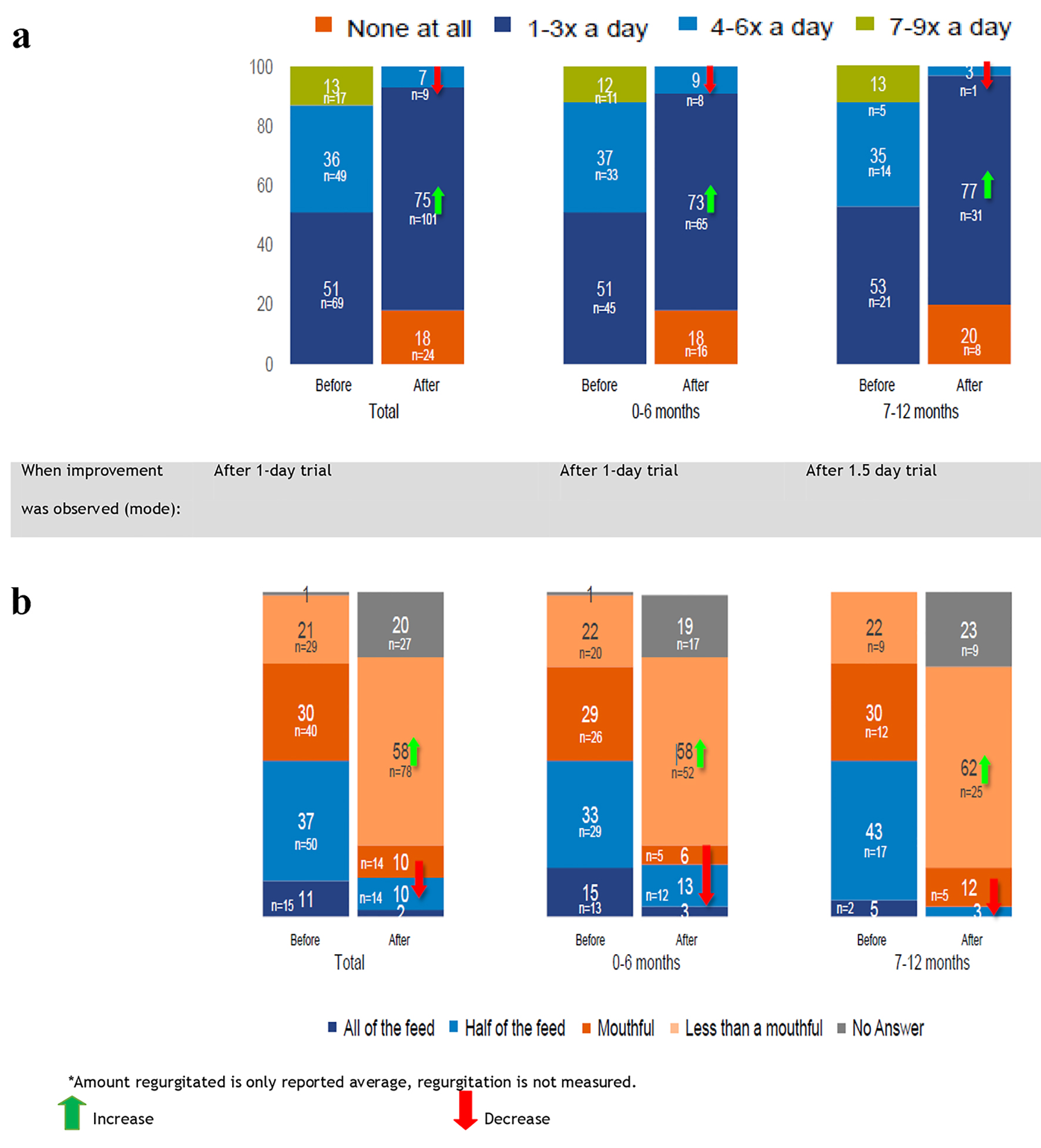
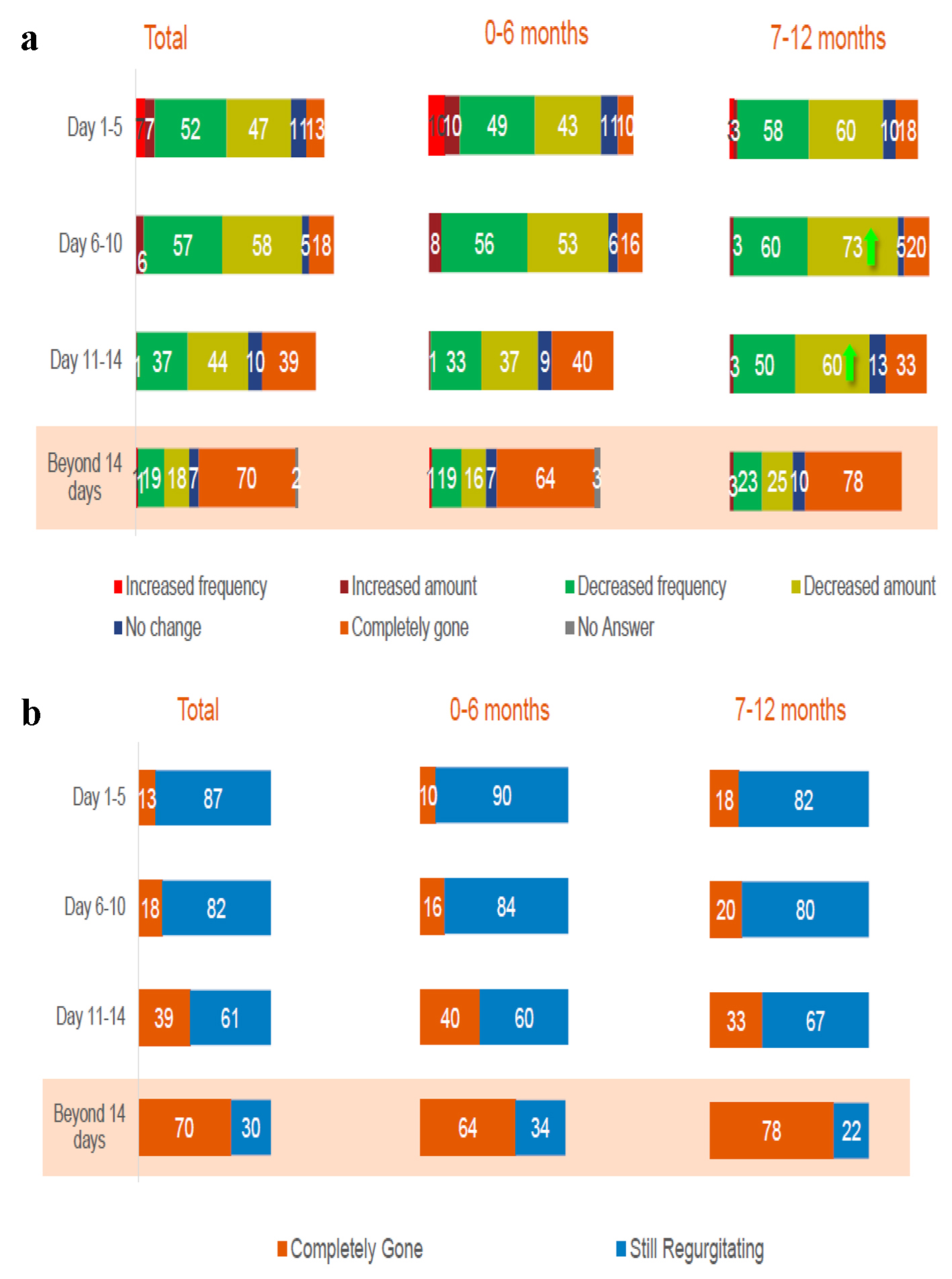
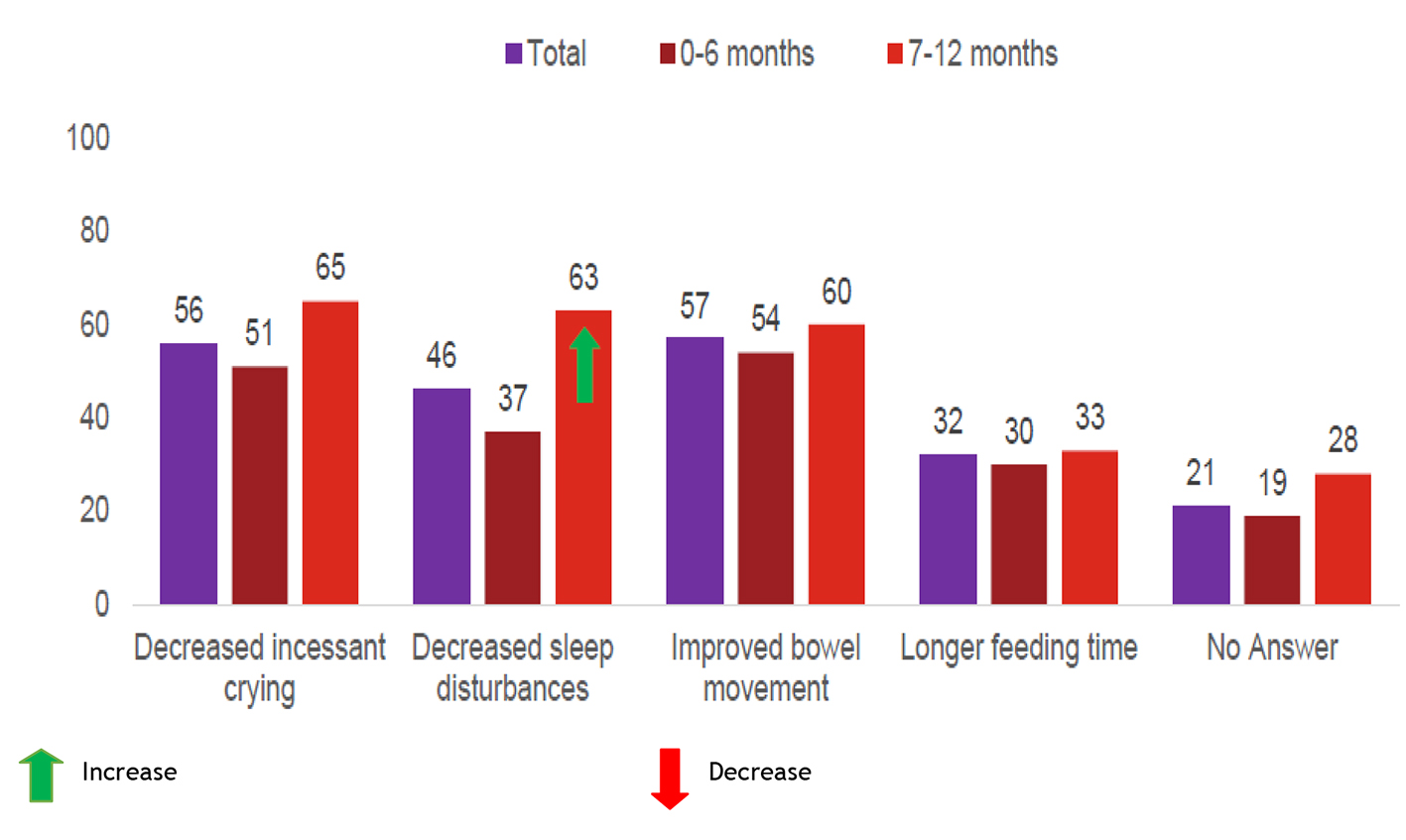
Table
| Ingredients | Unit | Per 100 g | Per 100 kcal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | g | 10.7 | 2.1 |
| Fat | g | 27.1 | 1.4 |
| Linoleic acid | mg | 3,415 | 676 |
| Alpha-linolenic acid | mg | 470 | 93 |
| AA | mg | 53 | 10 |
| DHA | mg | 53 | 10 |
| Lactose | g | 51.2 | 10.1 |
| Galacto-oligosaccharides | g | 0.4 | 0.08 |
| Galactomannan | g | 2.5 | 0.5 |
| Mineral | |||
| Calcium | mg | 385 | 76 |
| Phosporus | mg | 215 | 43 |
| Sodium | mg | 165 | 33 |
| Iron | mg | 5.0 | 0.99 |
| Copper | µg | 380 | 75 |
| Potassium | mg | 560 | 111 |
| Chloride | mg | 335 | 66 |
| Magnesium | mg | 49 | 97 |
| Zinc | mg | 4.4 | 0.87 |