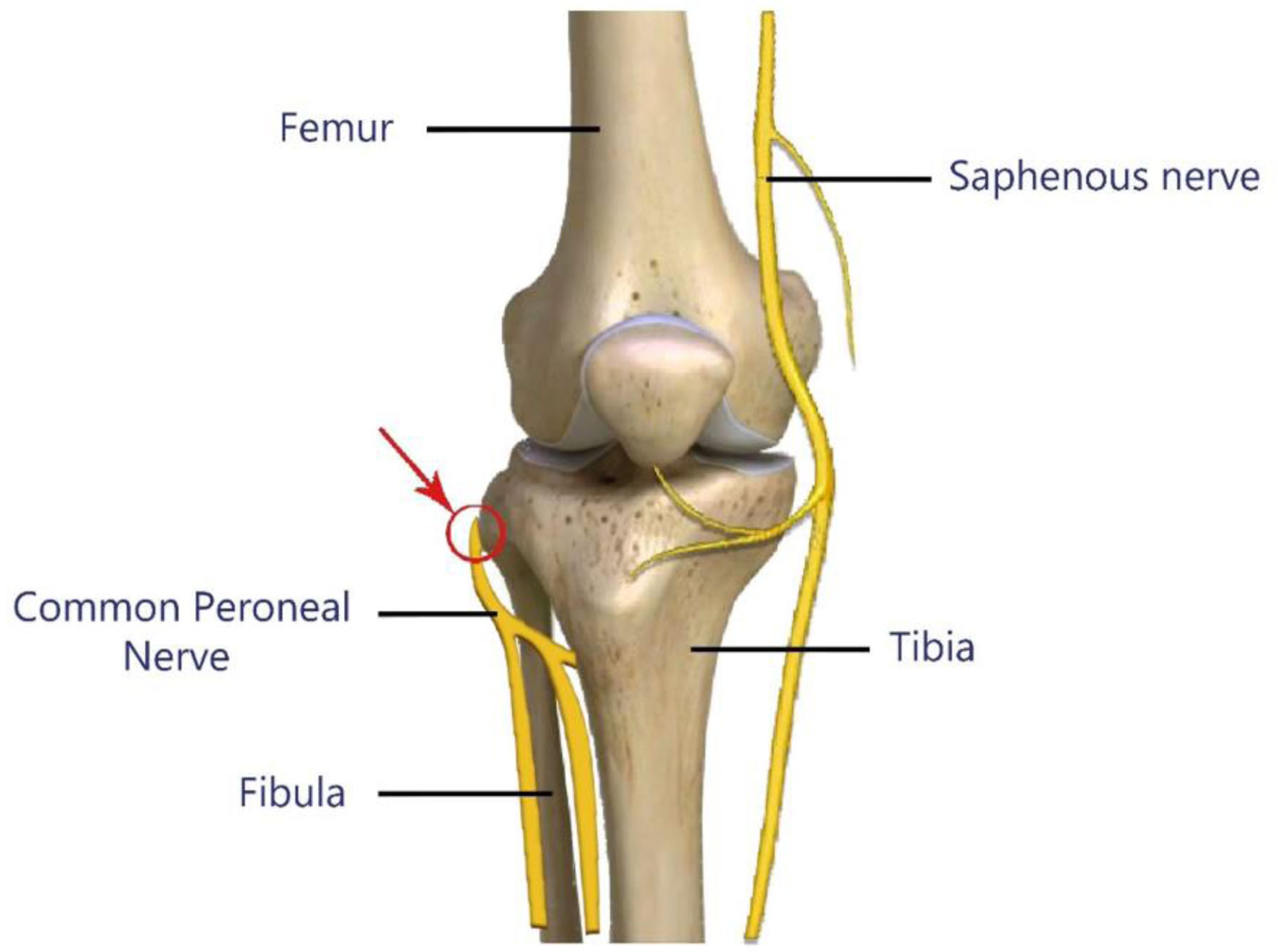
Figure 1. Common site of common peroneal nerve compression during positional injury (arrow and red circle).
| International Journal of Clinical Pediatrics, ISSN 1927-1255 print, 1927-1263 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Int J Clin Pediatr and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.theijcp.org |
Case Report
Volume 12, Number 1, May 2023, pages 15-21
Foot Drop Following Epidural Catheter Placement for Postoperative Analgesia Following Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in an Adolescent: Investigation and Etiology
Figures

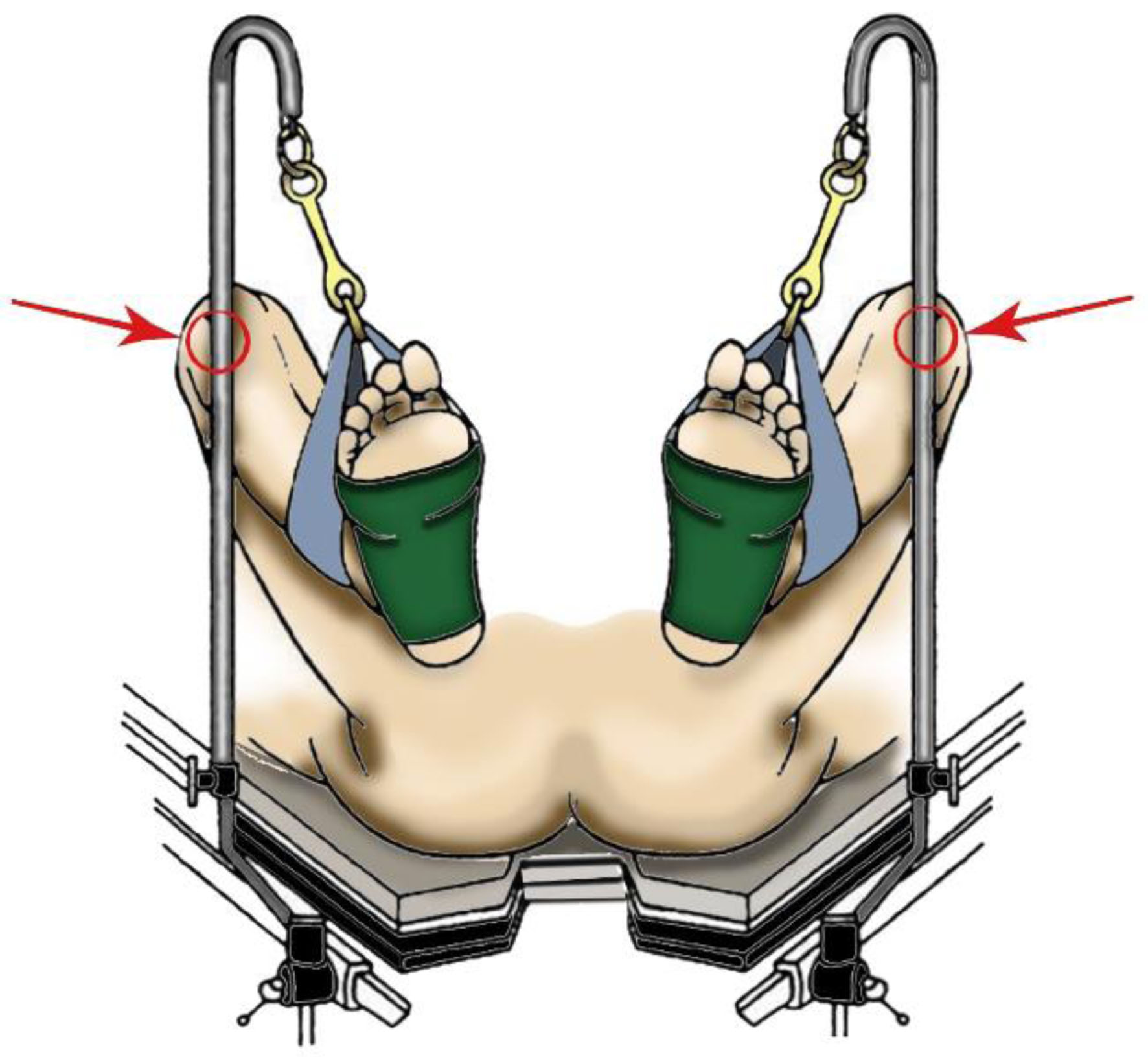
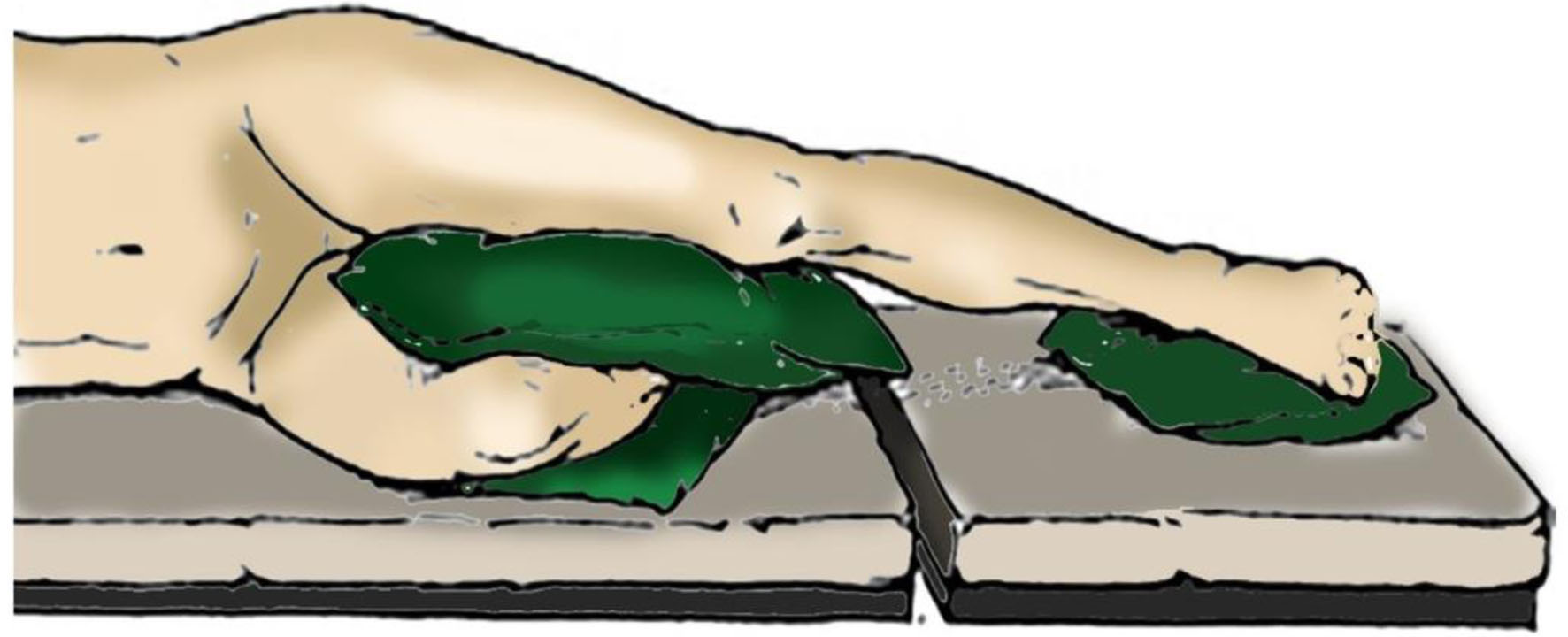
Table
| Authors and reference | Surgical procedure, duration, type of anesthesia, and positioning | Findings and outcome |
|---|---|---|
| CT: computed tomography; EMG: electromyogram; L: lumbar; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; POD: postoperative day. | ||
| Singh et al [20] | Closing wedge osteotomy of left congenital talipes equinovarus (90 min). General anesthesia with epidural catheter (L3-4). Supine position. | Right foot numbness. Epidural catheter removed. Foot drop developed within 48 h after catheter removal. MRI not possible due to cochlear implant. Complete motor recovery with occasional calf and shin paresthesia for 6 months. |
| Yigit et al [21] | Ureteroneocystostomy (4 h). General anesthesia with lumbar epidural catheter (level not noted). Supine position. | After 2 days of postoperative analgesia, epidural catheter removed. Patient noted to have bilateral ankle weakness without sensory loss. EMG showed focal demyelination of the peroneal nerve bilaterally at the level of the fibular head. |
| Nirmala and Kumari [22] | Diagnostic laparoscopy (35 min). Spinal anesthesia. Position: not mentioned. | Four hours after surgery, right foot drop noted. Normal MRI. Complete recovery in 8 weeks with conservative therapy. |
| Ahmad et al [23] | Elective cesarean section. Spinal anesthesia. Supine position. | Inability to move right ankle after surgery. One month later, right foot drop, numbness in right lateral aspect of her ankle, absent deep tendon reflex, and high step gait. MRI showed low lying spinal cord with tip at L4 and a fatty filum terminale. MR myelogram revealed a longitudinal syrinx at L1-3. Significant motor recovery 4/5 after 6 months. |
| Dorjey [24] | Emergency cesarean section (30 min). Spinal anesthesia (After fifth attempt). Supine position. | Bilateral foot drop 4 h after surgery, bilateral loss of deep tendon reflex, high step gait, and sensory impairment (L3-S1). MRI not available. Ultrasound showed no hematoma or soft tissue swelling. Treatment with methylprednisolone, thiamine, vitamin B12, and physiotherapy were initiated. Full right foot recovery at 4 months and full left foot recovery at 4 weeks. |
| Kantekin et al [25] | Emergency appendectomy procedure. Spinal anesthesia. Supine position. | Left ankle weakness developed 6 h postoperatively. MRI, CT, and EMG were normal. Treatment with gabapentin, vitamin B12, and physiotherapy. Able to walk without support by POD 70. |
| Lin et al [26] | Cesarean section. Combined lumbar spinal-epidural anesthesia. Supine position. | Right ankle weakness noted postoperatively. Epidural catheter removed. One month later, nerve conduction velocity showed right superficial peroneal nerve damage. Two months later, MRI showed perineural cysts bilaterally at S1 and S2 nerves. Complete recovery achieved within 3 months with conservative therapy. |
| Chen et al [27] | Cesarean section. Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia. Supine position with left lateral tilt. | At 30 h postoperatively, weakness noted in both lower extremities. Epidural catheter immediately removed. Six hours later, fecal and urinary incontinence. MRI showed thickening and clumping of the cauda equina nerve roots at L2-3 level (arachnoiditis). Treatment with high-dose corticosteroids, hyperbaric oxygen, and acupuncture. Foot drop persisted after 2 years of rehabilitative treatment. |